This approach ensures the rules meet market needs and are workable for financial info preparers. The FASB helps shape worldwide accounting by working with bodies like the IASB. This effort supports global business and investment by what does the fasb do offering universal high-quality financial reporting norms. Their goal is to keep accounting standards consistent and tackle new issues effectively.

Access Exclusive Templates
- Entities may use non-GAAP methods to give investors and analysts a clearer picture of their financial position or to help them make decisions about the direction of their business.
- GAAP is a set of standards that companies, nonprofits, and governments should follow when preparing and presenting their financial statements, including any related party transactions.
- If a corporation’s stock is publicly traded, its financial statements must follow rules set by the U.S.
- Take the guesswork out of your financial reporting and request a demo today.
- FASB’s strict standards ensure financial statements are transparent and comparable.
- Consistent financial reports also help company leaders monitor performance month over month and conduct competitive analyses with other publicly traded organizations.
- The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) sets the accounting standards needed for businesses in the U.S.
Initial efforts to how is sales tax calculated establish uniform financial reporting practices date back to 1917 when the Federal Reserve Board (FRB) published its bulletin “Uniform Accounting.” However, these efforts were halted due to the economic turbulence of the 1930s. The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) is an independent organization responsible for establishing and improving accounting standards, known as Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), within the United States. Professionals undergo years of education in order to truly understand the already existing principles and accounting standards.
Financial Accounting Standards Board – Explained
The diversity and experience of board members bring balance, ensuring terms end by 2027. The FASB currently boasts over 60 staff members that are collectively responsible for assisting the board members in their accounting and financial reporting duties. The staff members cooperate with the FASB Board as well as various project resource groups, partake in research activities, participate in roundtable meetings and scrutinize suggestions received from the public.
GAAP vs. IFRS

Since it started, FASB has updated many accounting rules, like ASC 606 and ASC 842. These updates make the accounting rules stronger and help companies keep up with the market and financial challenges. The goal is to have FASB standards match international ones, reducing differences in financial reports. The non-profit FASB is funded primarily through accounting support fees, which are paid by U.S. corporations that issue publicly traded securities. This funding method was written into the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, as amended (the Sarbanes-Oxley Act).
This is done by regularly updating accounting standards to match business changes. Subsequent attempts to create consistent reporting standards continued over the decades, but none were fully successful until the formation of the Wheat Committee in 1971. The committee, led by Francis Wheat, published a report in March 1972 that recommended a new, independent structure for setting accounting standards. This new structure included the establishment of the Financial Accounting Foundation (FAF), the Financial Accounting Standards Advisory Council (FASAC), and the FASB. The Financial Accounting Standards Board develops financial accounting standards and reporting practices.
FASB is the organization responsible for setting accounting guidelines laid out in GAAP. FASB plays a crucial role in continually updating and improving GAAP to respond to changes in business practices, financial markets, and regulatory requirements, so financial reporting remains reliable and relevant. The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) is known for improving financial reporting quality.
- In essence, the SEC provides oversight to ensure public companies and other market participants operate fairly.
- In recent years, the FASB has been working with the IASB on an initiative to improve financial reporting and the comparability of financial reports globally.
- Accruing tax liabilities in accounting involves recognizing and recording taxes that a company owes but has not yet paid.
- This new structure included the establishment of the Financial Accounting Foundation (FAF), the Financial Accounting Standards Advisory Council (FASAC), and the FASB.
- This is when FASB and the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) promised to make GAAP and International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) work together.
- Subsequent attempts to create consistent reporting standards continued over the decades, but none were fully successful until the formation of the Wheat Committee in 1971.
- Errors and omissions can impact a company’s credibility with lenders, investors, and other parties who rely on financial statements for an accurate picture of a company’s finances.
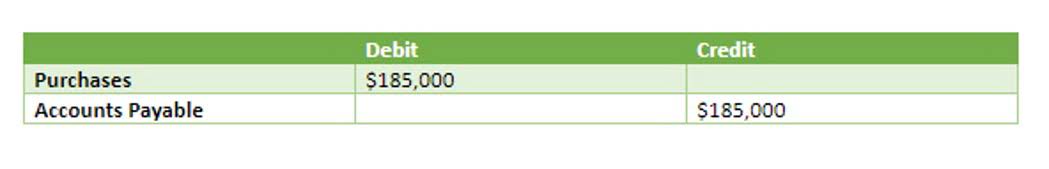
They are also responsible for formulating recommendations and creating drafts of documents for consideration by the Board members. In 2009, the FAF launched the FASB Accounting Standards Codification, an online research tool designed as a single source for authoritative, nongovernmental, generally accepted accounting principles in the United States. A “basic view” version is free, while the more comprehensive “professional view” is available by paid subscription. Companies can present certain figures without following GAAP guidelines, as long as they identify them as non-GAAP.
GAAP is meant to ensure consistency, accuracy, and transparency in financial reporting and aims to QuickBooks ProAdvisor provide a reliable foundation for investors to make informed decisions. While the rules established under GAAP generally improve the transparency in financial statements, they don’t guarantee that a company’s financial statements are free from errors or omissions meant to mislead investors. Always scrutinize financial statements, as there can still be room for manipulation within the framework of GAAP. Backing them are over 60 staff members and initiatives like the Emerging Issues Task Force (EITF) from 1984.